日常 Android 开发过程中,我们总需要在各个 module 中依赖各种第三方远程组件,像下面这样:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
implementation 'org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib:1.4.32'
implementation 'androidx.core:core-ktx:1.6.0'
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.3.0'
implementation 'com.google.android.material:material:1.4.0'
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:2.0.4'
implementation 'androidx.legacy:legacy-support-v4:1.0.0'
implementation 'com.google.dagger:hilt-android:2.36'
implementation 'androidx.hilt:hilt-lifecycle-viewmodel:1.0.0-alpha03'
kapt 'com.google.dagger:hilt-android-compiler:2.36'
implementation 'org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:1.5.0'
implementation 'androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx:2.3.1'
如果不对这些依赖的版本进行优雅的管理就会导致版本升级时各种全局搜索和替换,也容易导致一些依赖版本冲突问题。那么如何对依赖版本做统一合理的管控呢?这里提供了三种常见方式,大家可选择性食用。
ext 属性方式
这种方式通过在根目录的 build.gradle 中创建一个 ext 区域来存放各组件的 version 值:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
ext {
kotlinVersion = "1.4.32"
coreKtxVersion = "1.6.0"
appcompatVersion = "1.3.0"
materialVersion = "1.4.0"
constraintlayoutVersion = "2.0.4"
legacySupportVersion = "1.0.0"
hiltVersion = "2.36"
hiltViewModelVersion = "1.0.0-alpha03"
coroutinesVersion = "1.5.0"
viewModelVersion = "2.3.1"
}
如此一来,我们就可以在每个 module 中引用声明好的组件版本了。使用的话也很简单,只需要在相应的 module 中采用字符串占位符替换即可:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
dependencies {
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib:${rootProject.ext.kotlinVersion}"
implementation "androidx.core:core-ktx:${rootProject.ext.coreKtxVersion}"
implementation "androidx.appcompat:appcompat:${rootProject.ext.appcompatVersion}"
implementation "com.google.android.material:material:${rootProject.ext.materialVersion}"
implementation "androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:${rootProject.ext.constraintlayoutVersion}"
implementation "androidx.legacy:legacy-support-v4:${rootProject.ext.legacySupportVersion}"
implementation "com.google.dagger:hilt-android:${rootProject.ext.hiltVersion}"
kapt "com.google.dagger:hilt-android-compiler:${rootProject.ext.hiltVersion}"
implementation "androidx.hilt:hilt-lifecycle-viewmodel:${rootProject.ext.hiltViewModelVersion}"
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:${rootProject.ext.coroutinesVersion}"
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx:${rootProject.ext.viewModelVersion}"
}
值得注意的地方有两点:
- 由单引号
''变成了双引号"" - 通过
$来引用版本属性值
虽然说这种方式很大程度上帮助我们统一了组件依赖版本管理,但是,此种方式并不支持 IDE 内的代码提示,导致每次都需要手动复制粘贴,多少可能还是会有一些人为的误操作情况出现。
buildSrc 模块
按照 Gradle 文档 所说:当运行 Gradle 时会检查项目中是否存在一个名为 buildSrc 的目录。然后 Gradle 会自动编译并测试这段代码,并将其放入构建脚本的类路径中, 对于多项目构建,只能有一个 buildSrc 目录,该目录必须位于根项目目录中, buildSrc 是 Gradle 项目根目录下的一个目录,它可以包含我们的构建逻辑,与脚本插件相比,buildSrc 应该是首选,因为它更易于维护、重构和测试代码。
首先需要在项目根目录下创建一个名为 buildSrc 的目录,然后执行 make project (Android studio工具栏小锤子)
Note:名字必须是
buildSrc,因为运行 Gradle 时会检查项目中是否存在一个名为 buildSrc 的目录 。
在 buildSrc 文件夹里创建名为 build.gradle.kts 的文件,添加以下内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
plugins {
`kotlin-dsl`
}
repositories{
jcenter()
}
在 buildSrc/src/main/java/包名/ 目录下新建 Dependencies.kt 文件,添加以下内容:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
/**
* Version config of libraries.
*/
object Versions {
const val kotlinVersion = "1.4.32"
const val coreKtxVersion = "1.6.0"
const val appcompatVersion = "1.3.0"
const val materialVersion = "1.4.0"
const val constraintlayoutVersion = "2.0.4"
const val legacySupportVersion = "1.0.0"
const val hiltVersion = "2.36"
const val hiltViewModelVersion = "1.0.0-alpha03"
const val coroutinesVersion = "1.5.0"
const val viewModelVersion = "2.3.1"
}
object Dependencies {
val kotlin = "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib:${Versions.kotlinVersion}"
val coreKtx = "androidx.core:core-ktx:${Versions.coreKtxVersion}"
val appcompat = "androidx.appcompat:appcompat:${Versions.appcompatVersion}"
val material = "com.google.android.material:material:${Versions.materialVersion}"
val constraintlayout = "androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:${Versions.constraintlayoutVersion}"
val legacySupport = "androidx.legacy:legacy-support-v4:${Versions.legacySupportVersion}"
val hilt = "com.google.dagger:hilt-android:${Versions.hiltVersion}"
val hiltViewModel = "androidx.hilt:hilt-lifecycle-viewmodel:${Versions.hiltViewModelVersion}"
val hiltProcessor = "com.google.dagger:hilt-android-compiler:${Versions.hiltVersion}"
val coroutines = "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:${Versions.coroutinesVersion}"
val viewModelKtx = "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx:${Versions.viewModelVersion}"
}
最终目录结构如下图所示:
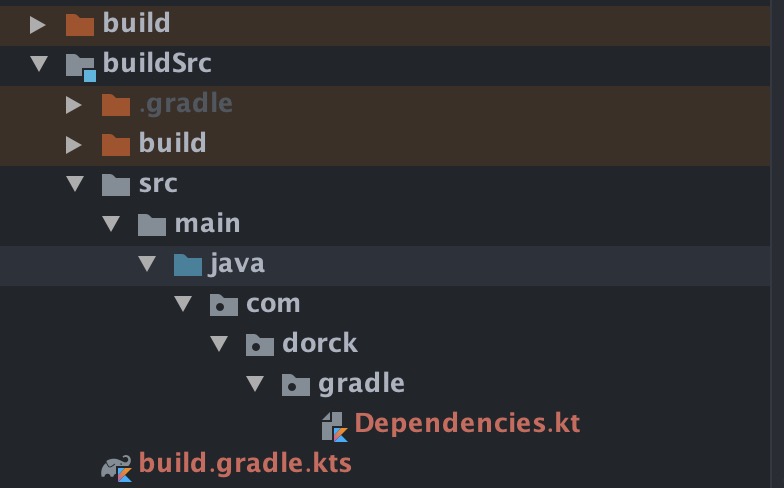
最后,只需要在我们自己的 module 中更改依赖版本源即可:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
dependencies {
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib:${Versions.kotlinVersion}"
implementation "androidx.core:core-ktx:${Versions.coreKtxVersion}"
implementation "androidx.appcompat:appcompat:${rootProject.ext.appcompatVersion}"
implementation "com.google.android.material:material:${Versions.materialVersion}"
implementation "androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:${Versions.constraintlayoutVersion}"
implementation "androidx.legacy:legacy-support-v4:${Versions.legacySupportVersion}"
implementation "com.google.dagger:hilt-android:${Versions.hiltVersion}"
kapt "com.google.dagger:hilt-android-compiler:${Versions.hiltVersion}"
implementation "androidx.hilt:hilt-lifecycle-viewmodel:${Versions.hiltViewModelVersion}"
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:${Versions.coroutinesVersion}"
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx:${Versions.viewModelVersion}"
}
当然我们也可以直接将各个组件依赖细节隐藏起来,通过以下方式直接调用:
1
2
3
4
5
dependencies {
implementation Dependencies.kotlin
implementation Dependencies.coreKtx
......
}
如此一来,我们不仅做到了组件依赖版本全局统一管理,同时也支持 Android Studio 自动补全,和普通的类中引用外部类的常量并无二致。但是,这个方案也并不是看似完美无缺的:
A change in buildSrc causes the whole project to become out-of-date. Thus, when making small incremental changes, the –no-rebuild command-line option is often helpful to get faster feedback. Remember to run a full build regularly or at least when you’re done, though.
以上说明来自 Gradle 官方文档,通俗来讲就是 buildSrc 的改动会导致整个项目的 rebuild,及其耗时。那么有没有一种方案可以做到增量更新呢?于是,Composing builds 呼之欲出了。
Composing build
A composite build is simply a build that includes other builds. In many ways a composite build is similar to a Gradle multi-project build, except that instead of including single projects, complete builds are included.
复合构建只是包含其他构建的构建。在许多方面,复合构建类似于 Gradle 多项目构建,不同之处在于:它包括完整的 builds ,而不是包含单个 projects。
它具有以下能力:
- 组合相对独立的构建,例如,在应用程序使用的库中尝试错误修复时
- 将大型的多项目构建分解为更小,更孤立的块,可以根据需要独立或一起工作
通俗来讲,我们使用 Composing build 主要用于隔离构建变化,让某个组件版本改动只会影响到单个 module,而不是整个项目,所以这里其实是将依赖版本管理“插件化”,从而每次版本变动只会影响到 plugin module。
首先,我们按照正常 gradle 插件创建流程来新建一个 module 为 version-plugin,并修改该 module 下的 build.gradle:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
apply plugin: 'kotlin'
apply plugin: 'java-gradle-plugin'
gradlePlugin {
plugins {
version {
id = 'com.dorck.version.plugin'
implementationClass = 'com.dorck.version.plugin.VersionPlugin'
}
}
}
buildscript {
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-gradle-plugin:1.6.10"
}
}
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
}
插件初始化完毕后,我们在插件的包名路径下创建 VersionPlugin.kt 和 config/VersionConfigs.kt 两个文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
package com.dorck.version.plugin.config
object VersionConfigs {
const val applicationId = "com.moosphon.android.daily"
const val compileSdkVersion = 30
const val buildToolsVersion = "30.0.3"
const val minSdkVersion = 21
const val targetSdkVersion = 30
const val versionCode = 1
const val versionName = "1.0"
const val kotlinVersion = "1.4.32"
const val coreKtxVersion = "1.6.0"
const val appcompatVersion = "1.3.0"
const val materialVersion = "1.4.0"
const val constraintlayoutVersion = "2.0.4"
const val legacySupportVersion = "1.0.0"
const val hiltVersion = "2.36"
const val hiltViewModelVersion = "1.0.0-alpha03"
const val coroutinesVersion = "1.5.0"
const val viewModelVersion = "2.3.1"
}
我们集中配置了包含编译版本、包名、应用版本及组件版本等信息,至于 VersionPlugin.kt 里面是空实现,不作说明。
然后,我们需要在 setting.gradle 中声明包含该插件:
1
2
// 版本管理插件
includeBuild('version-plugin')
最终,在上层 module 中使用即可:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
import com.dorck.version.plugin.config.VersionConfigs
plugins {
id 'com.android.application'
id 'kotlin-android'
id 'kotlin-android-extensions'
id 'kotlin-kapt'
// 组件依赖版本管理
id 'com.dorck.version.plugin'
}
android {
compileSdkVersion VersionConfigs.compileSdkVersion
buildToolsVersion VersionConfigs.buildToolsVersion
defaultConfig {
applicationId VersionConfigs.applicationId
minSdkVersion VersionConfigs.minSdkVersion
targetSdkVersion VersionConfigs.targetSdkVersion
versionCode VersionConfigs.versionCode
versionName VersionConfigs.versionName
testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
kotlinOptions {
jvmTarget = '1.8'
}
viewBinding {
enabled = true
}
}
dependencies {
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib:${VersionConfigs.kotlinVersion}"
implementation "androidx.core:core-ktx:${VersionConfigs.coreKtxVersion}"
implementation "androidx.appcompat:appcompat:${VersionConfigs.appcompatVersion}"
implementation "com.google.android.material:material:${VersionConfigs.materialVersion}"
implementation "androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:${VersionConfigs.constraintlayoutVersion}"
implementation "androidx.legacy:legacy-support-v4:${VersionConfigs.legacySupportVersion}"
implementation "com.google.dagger:hilt-android:${VersionConfigs.hiltVersion}"
kapt "com.google.dagger:hilt-android-compiler:${VersionConfigs.hiltVersion}"
implementation "androidx.hilt:hilt-lifecycle-viewmodel:${VersionConfigs.hiltViewModelVersion}"
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:${VersionConfigs.coroutinesVersion}"
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx:${VersionConfigs.viewModelVersion}"
}
通过简单对比 buildSrc 和 Composing build 两种方式发现:后者编译速度明显高于前者,毕竟它将影响范围控制在了单个 module,而不是前者的整个Project。此外,这两种方式都支持 IDE 中代码提示自动补全。
相关参考
许可协议: 署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际 转载请保留原文链接及作者。